Understanding Liberty: Negative vs. Positive
Liberty is a concept that has intrigued philosophers for centuries, and Isaiah Berlin famously distinguished between two types: negative liberty and positive liberty. This blog post explores these concepts in depth, illustrating their implications through relatable examples and discussing their relevance in today's society.
Introduction to Two Concepts of Liberty
When we think about freedom, we often view it as the ability to act without constraints. However, the reality is that one person's freedom can inadvertently affect another's. To navigate this complex landscape, rules and structures are often established. Berlin's distinction between negative and positive liberty sheds light on how we understand freedom and the necessary balance between individual autonomy and societal constraints.
Negative Liberty
Negative liberty is fundamentally about freedom from interference. It describes an individual's right to be free from external constraints and the absence of obstacles within society. Imagine a person living in a community where the government imposes few restrictions — this is a clear representation of negative liberty.
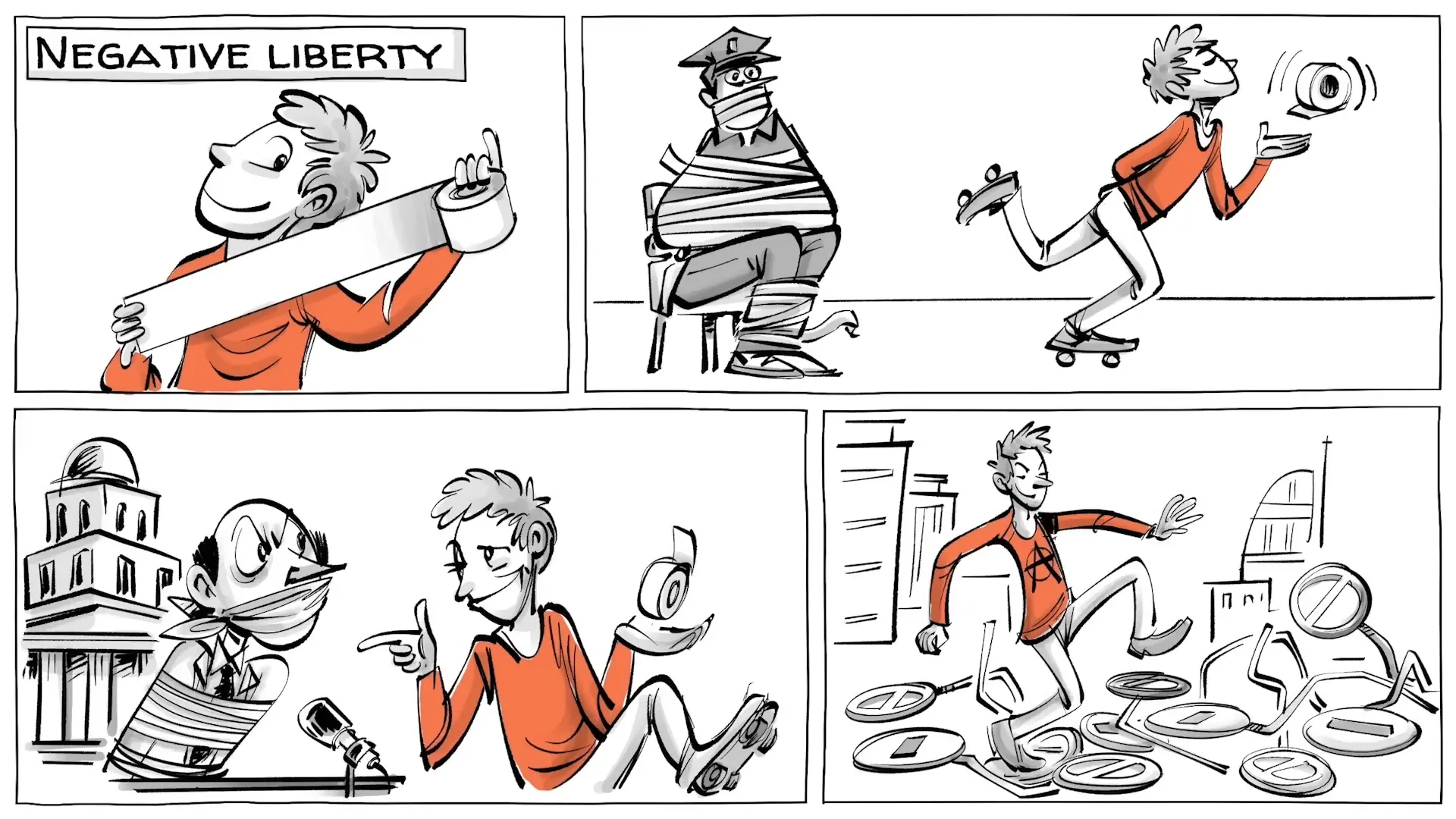

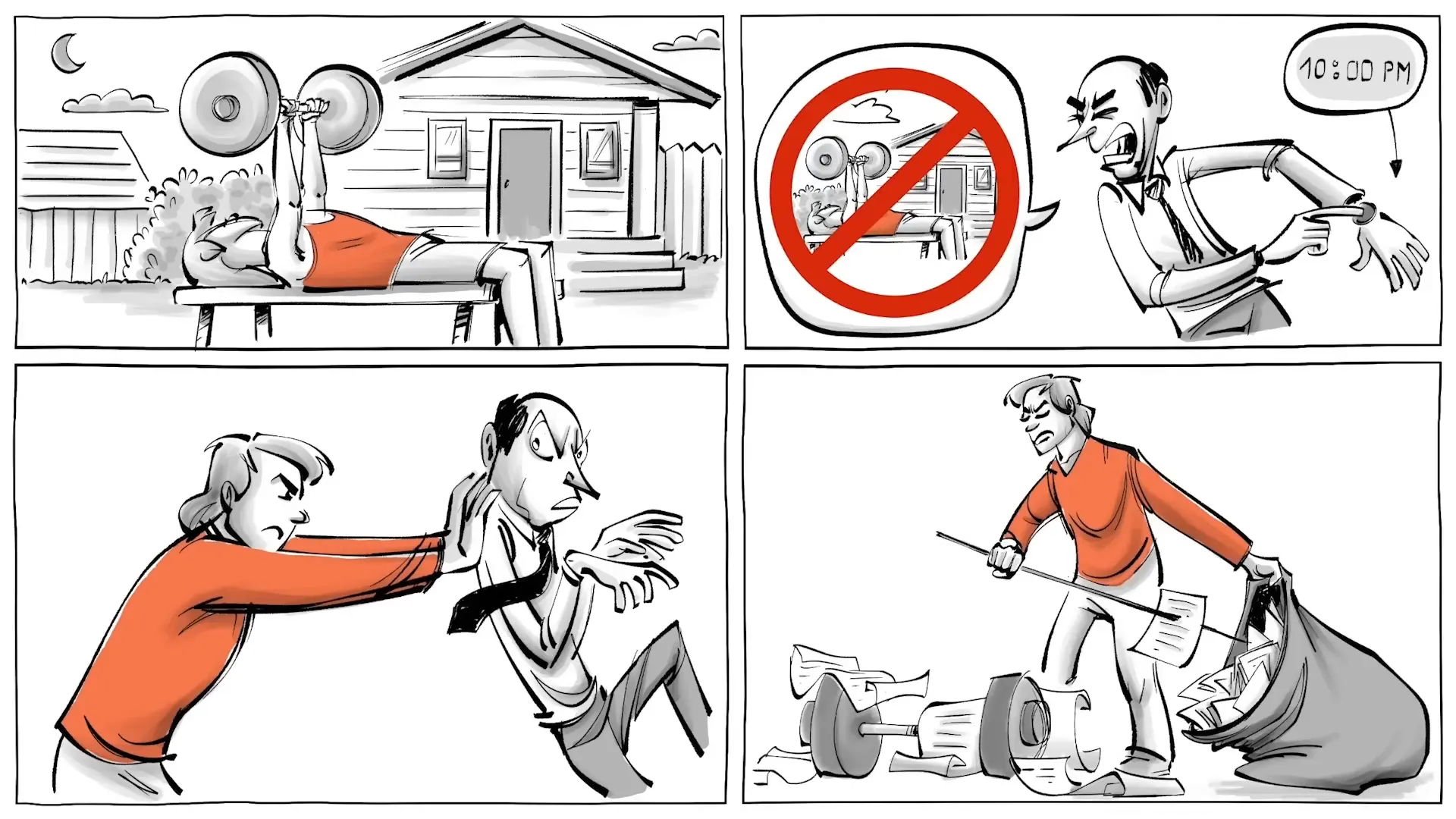
Let’s consider Frank, a character who embodies the principles of negative liberty. Frank lives in a place called Freeland where he values his health and family above all else. He rises early to maintain his fitness routine and prioritizes his children’s education. However, he resents the government’s role in his life, particularly the taxes that fund public healthcare. For him, these taxes are an infringement on his freedom.
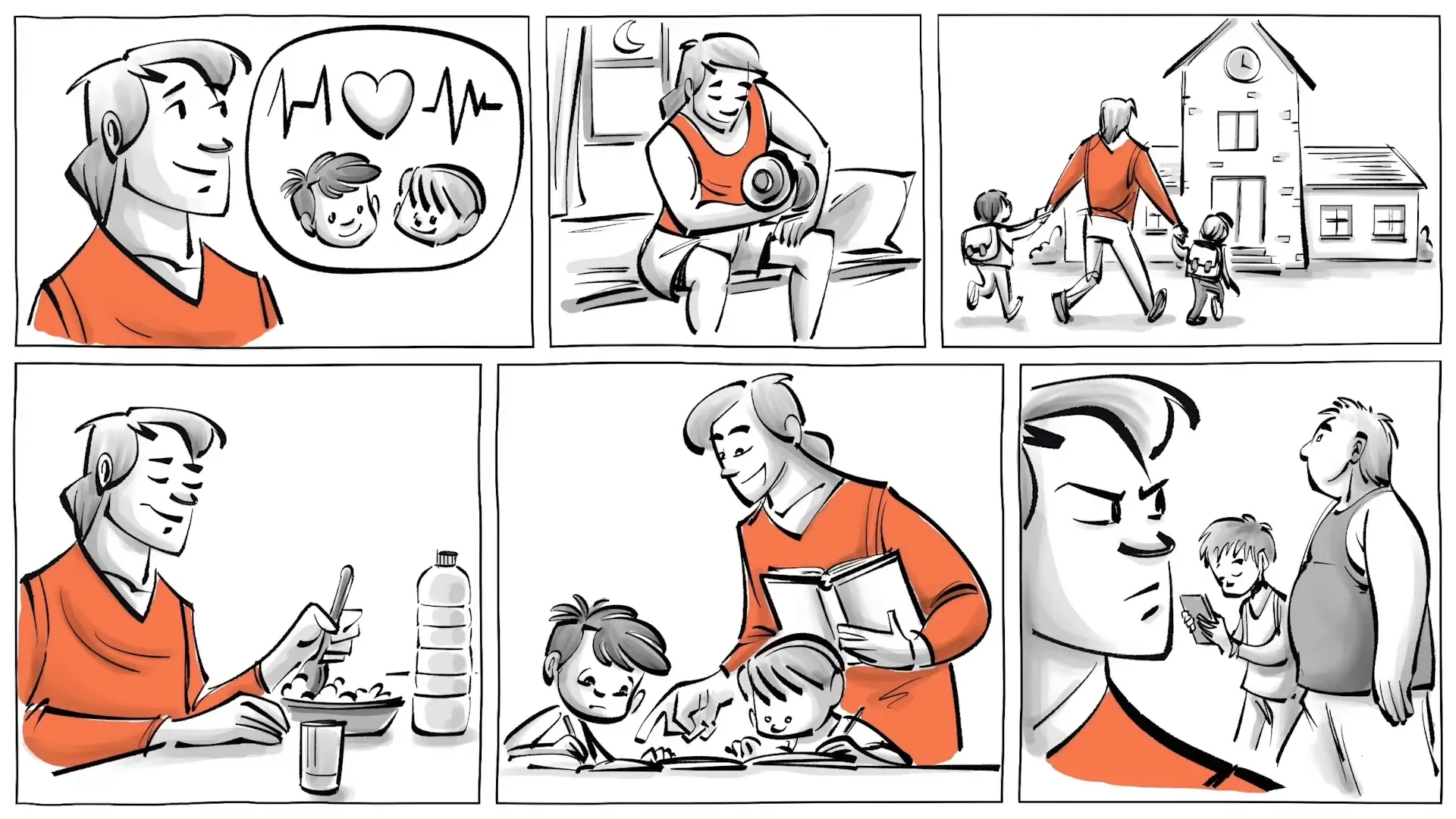

Moreover, Frank enjoys working out late at night in front of his house, but Freeland has recently prohibited such activities after 10 PM. This law feels like an intrusion into his personal life, and Frank's desire for freedom from government regulations grows stronger. He also believes that public schools are ineffective and wishes to homeschool his children, yet this is illegal in Freeland. Frustrated, Frank ultimately decides to move to Liberty, a place he believes offers greater freedom from such external constraints.
Positive Liberty
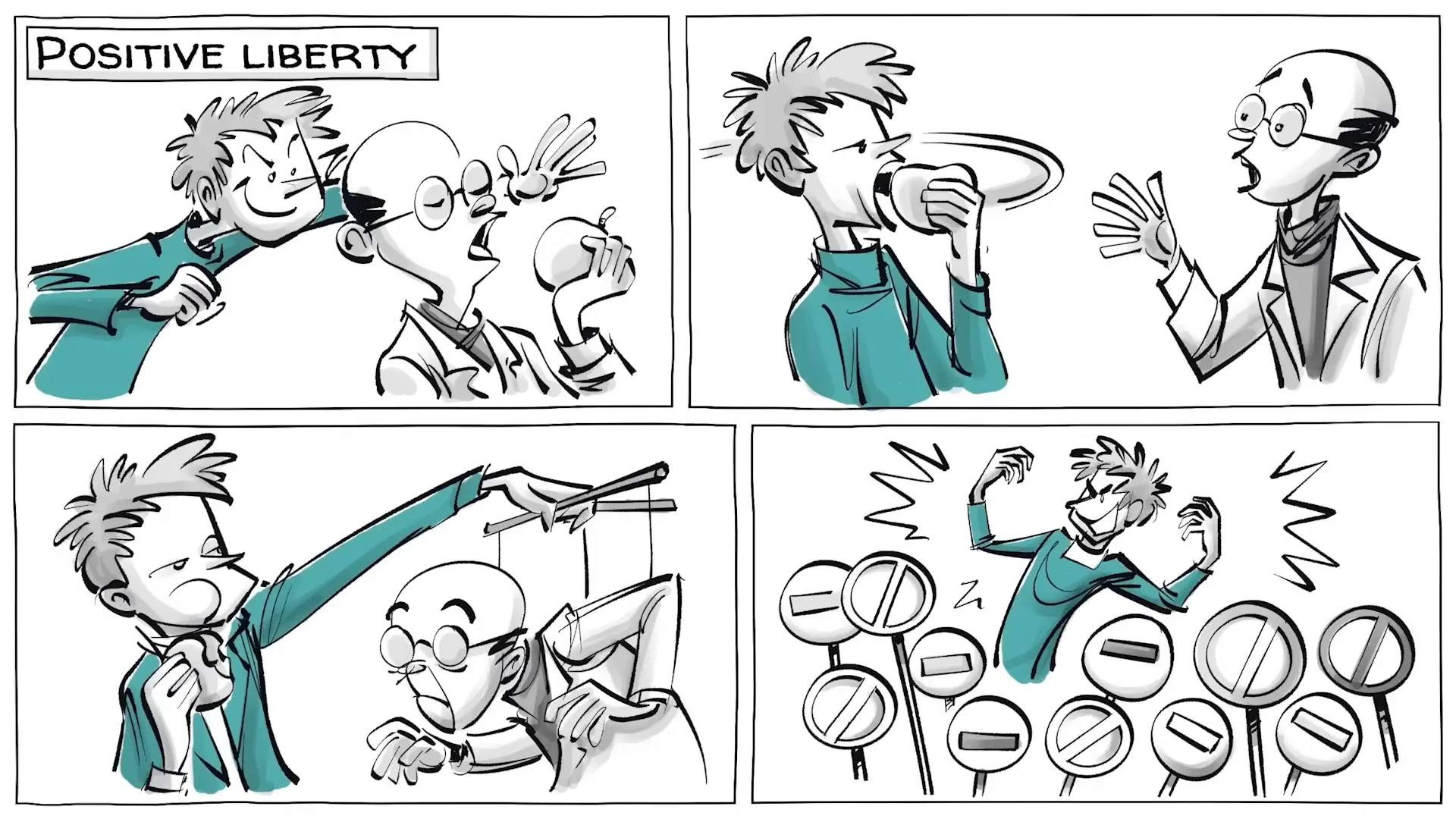
In contrast, positive liberty is about the freedom to act — the ability to take control of one’s life and to pursue one's own goals. It encompasses the idea that true freedom requires not just the absence of constraints but the presence of conditions that allow individuals to realize their potential. This concept is more about empowerment than mere absence of interference.

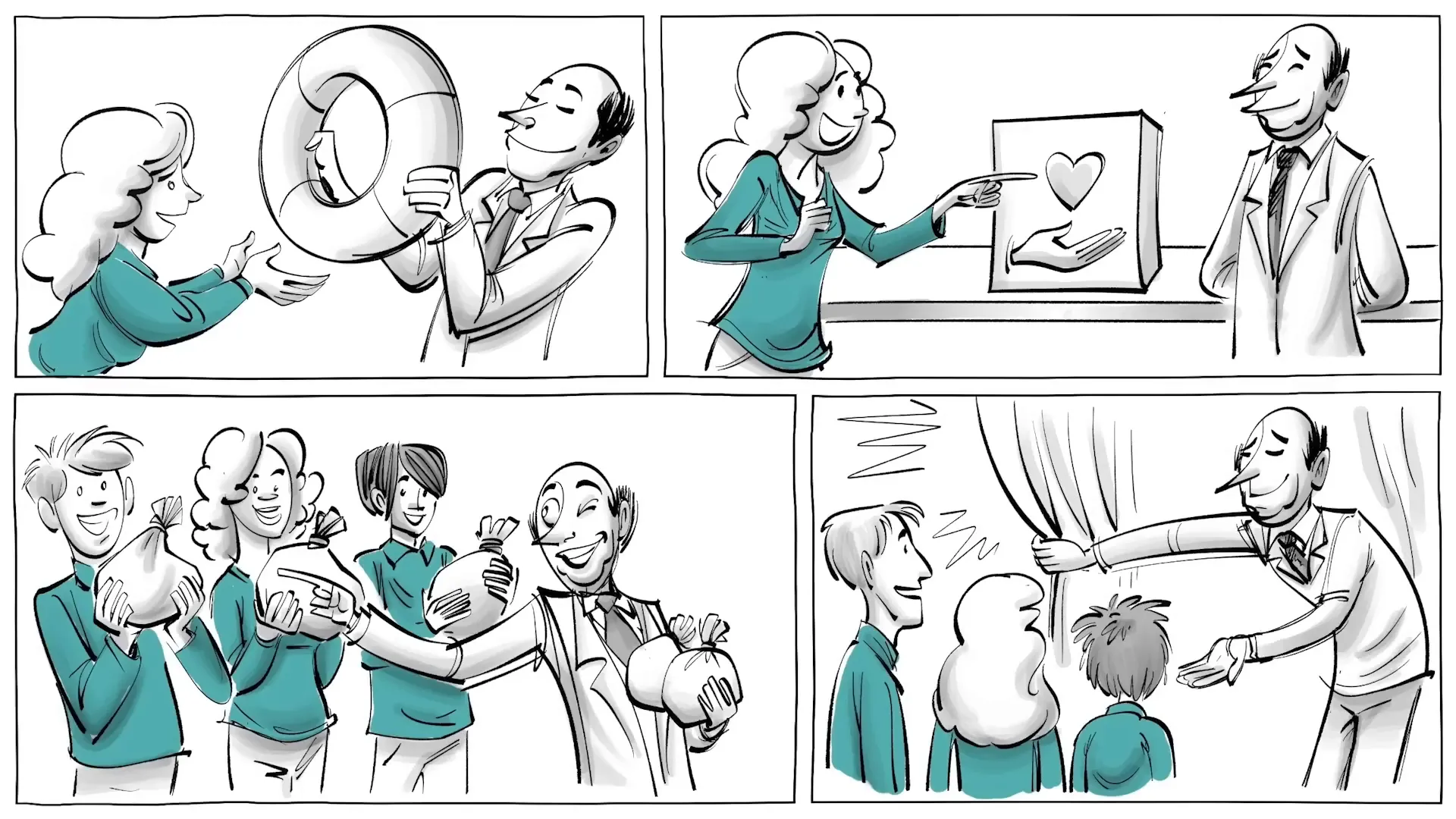
Lilly, another character in our discussion, lives in Liberty where she values justice and dreams of becoming a judge. However, her experience starkly contrasts with Frank’s. After an accident leaves her in need of surgery, she discovers that medical care is prohibitively expensive in Liberty. Lilly feels she lacks the freedom to access the necessary healthcare services, highlighting a critical aspect of positive liberty — the structural limitations present in society that can impede an individual’s ability to thrive.
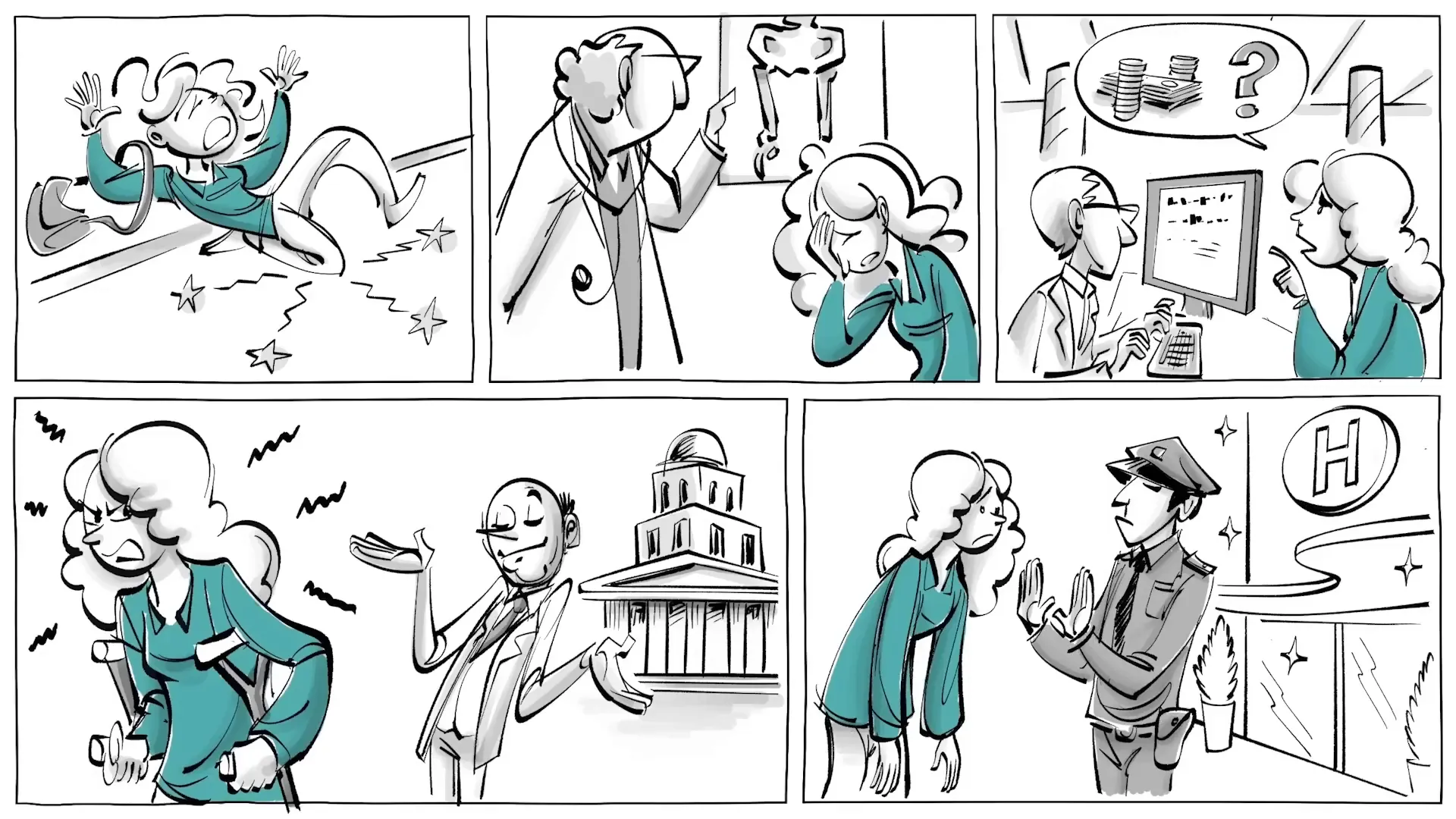

As Lilly recovers from her surgery, she finds the environment in Liberty stifling. The air pollution from cars makes it difficult for her to rehabilitate properly, and she feels trapped by her circumstances. Her aspiration to attend university is further hindered by her disadvantaged background, leaving her feeling frustrated and powerless. This lack of access to opportunities underscores the necessity of positive liberty — having the means to pursue one’s goals and dreams.
Clash of Ideologies
The ideological divide between proponents of negative liberty and those who champion positive liberty is significant. Supporters of negative liberty, often aligned with classical libertarian ideals, view the state as a coercive force that restricts individual freedom. They advocate for minimal government intervention, low taxes, and fewer regulations, believing that individuals should be free to make their own choices without external interference.
On the other hand, advocates of positive liberty identify more with social liberalism. They argue for a robust welfare state that ensures fair distribution of resources and equal access to opportunities. This perspective emphasizes the need for societal structures that empower individuals to overcome obstacles and realize their potential.
What Do You Think?
As we reflect on these two forms of liberty, it’s essential to consider which kind resonates more with you personally. Do you value the freedom from constraints, or do you believe that true freedom also requires the ability to act and access opportunities? Berlin’s theory prompts us to think critically about our own definitions of liberty and the balance between negative and positive aspects in our lives.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the distinction between negative and positive liberty is crucial in navigating the complexities of freedom in society. Both concepts offer valuable insights into the nature of individual rights and the role of government. As we engage in discussions about liberty, it’s essential to recognize the importance of both perspectives and how they shape our understanding of freedom in the modern world.



